Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a prevalent oral health issue. It affects millions of people worldwide. It ranges from mild gum inflammation (gingivitis) to severe infections that can damage the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. Understanding how to recognize, prevent, and manage gum disease is essential. Let’s discuss how to maintain a healthy mouth and preventing tooth loss.
Recognizing Periodontal Disease
-
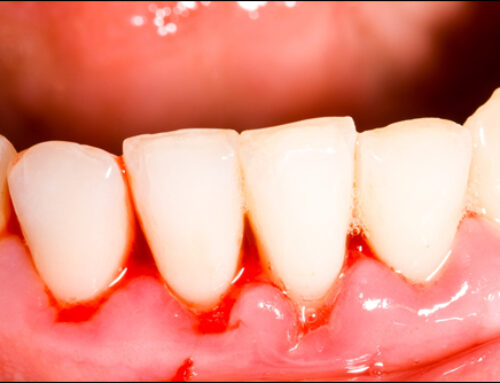
- Early Signs and Symptoms: The initial stage of gum disease is gingivitis. It is characterized by red, swollen gums that may bleed easily during brushing or flossing. Other early symptoms include persistent bad breath, gum tenderness, and a receding gum line. While gingivitis is often painless, if left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis.
- Advanced Symptoms: As gum disease advances to periodontitis, more severe symptoms may appear, including loose or shifting teeth, painful chewing, and the formation of deep pockets between the teeth and gums. These pockets can harbor bacteria, leading to further inflammation and bone loss around the teeth.
 Preventing Periodontal Disease
Preventing Periodontal Disease
-
- Good Oral Hygiene Practices: Maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine is key to preventing gum disease. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, focusing on the gum line, and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between teeth. Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can also help reduce bacteria and prevent gum inflammation.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Schedule regular dental visits for professional cleanings and check-ups. Dentists can remove tartar, a hardened form of plaque that cannot be removed by brushing alone, and identify early signs of gum disease. Early intervention is crucial for preventing the progression of gum disease.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of periodontal disease. Avoid smoking and tobacco use, which are major contributors to gum disease. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports oral health and strengthens the immune system, helping your body fight off infections.
Managing Periodontal Disease
-
- Professional Treatments: If periodontal disease is detected, your dentist may recommend scaling and root planing, a deep-cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smooths the root surfaces to promote healing. In more advanced cases, surgical interventions such as flap surgery or bone grafts may be necessary to restore damaged tissue and bone.
- Ongoing Maintenance: After treatment, maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial to prevent the recurrence of periodontal disease. Regular follow-up appointments with your dentist are essential to monitor your gum health and ensure the disease is under control. Your dentist may recommend additional treatments, such as antibiotics or antimicrobial mouth rinses, to manage inflammation and prevent infection.
Periodontal disease is a serious oral health condition that can lead to significant complications if left untreated. By recognizing the signs and symptoms, practicing good oral hygiene, and seeking regular dental care, you can prevent and effectively manage gum disease. Early intervention and a commitment to healthy lifestyle choices are essential for maintaining healthy gums and teeth. If you experience any symptoms of periodontal disease, consult your dentist promptly to receive appropriate treatment and protect your oral health.